Section outline
-
Iterative design process
Students should be aware of, and able to explain, different approaches to user centred design. That in approaching a design challenge there is not a single process, but that good design always addresses many issues, including:
• designing to meet needs, wants or values
• investigations to inform the use of primary and secondary data:
• market research
• interviews
• human factors
• focus groups
• product analysis and evaluation
• the use of anthropometric data and percentiles
• the use of ergonomic data
• the development of a design proposal
• the planning and manufacture of a prototype solution
• the evaluation of a prototype solution to inform further development. -
Design influences
Students should be aware of, and able to discuss, how key historical design styles, design movements and influential designers that have helped to shape product design and manufacture.
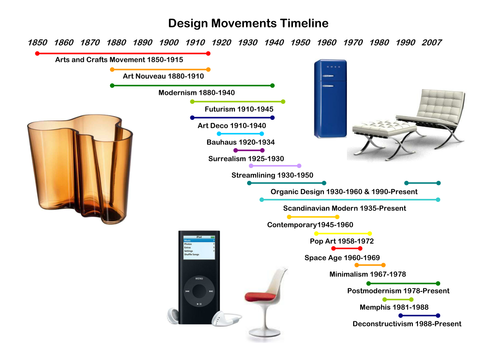
Design styles and movements
Students should be aware of, and be able to discuss, key design styles and movements and their principles of design, including:
Arts and craft movement
Art Deco
Modernism, eg Bauhaus
Post modernism, eg Memphis
Designers and their work
Students should be aware of, and be able to discuss, the work of influential designers and how their work represents the principles of different design movements, including:
Phillipe Starck
James Dyson
Margaret Calvert
Dieter Rams
Charles and Ray Eames
Marianne Brandthttp://www.core77.com/posts/36776/Marianne-Brandt-Bauhaus-Powerhouse
Weblinks
http://www.vam.ac.uk/page/0-9/20th-century-design-styles/
http://www.stedmunds.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/05/Design-Movements-Timeline.pdf
http://www.vam.ac.uk/page/a/art-nouveau/